Data is a huge part of our modern lives. We are constantly accessing, using, and creating data. The Internet’s existence is dependent upon sharing it and the largest companies on the Internet generate immense wealth from it. Its value makes it a target of unscrupulous individuals and organizations that try to benefit from trading in it illegally.
Data Protection vs. Data Security
There are two aspects of data security that your translation provider must pay attention to privacy protections of individuals’ information and overall security of data that is collected by them.
If your company is based in the EU, your translation provider must comply with GDPR guidelines. Regarding data security, they must be able to show that they follow processes and utilize technology that protects data from unauthorized access. This can most easily be demonstrated by your translation provider if they have ISO 27000 certification or a SOC certification.
Free Machine Translation Tools and Their Risk
One of the most common areas of data insecurity involves the use of free machine translation tools such as Google Translate or Microsoft Translator. Regardless of who is employing these tools, your company or your translation provider, the risk could be the same.
In 2017, the most infamous case of a data breach caused using free machine translation (MT) services involved the site Translate.com, whose free, online MT page, which used Microsoft Translator. Norwegian News Agency (NRK) revealed in a report that state-run oil giant, Statoil, had discovered that sensitive corporate information that had been passed through Translate.com’s online service was made public and became searchable on the open Internet using Google.
For example, Google explains in their policies that it gives itself the right to use and publish your data as part of using these services. By using the service, you tacitly agree to these terms.
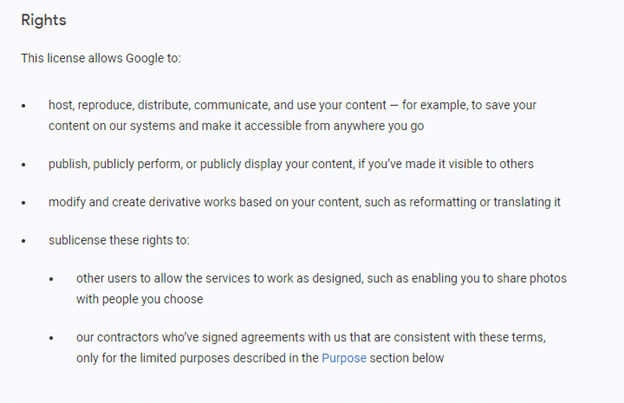
Organizations need to be aware of these security holes when using free, publicly available tools. It is possible to have the convenience and ease of use of these tools by engaging a capable partner who can configure and deploy secure instances of MT technology.
How to Use Free Machine Translation Tools
We recommend that you establish a corporate policy governing the use or non-use of free MT tools. The easiest thing is to prohibit their use by employees. Albeit inconvenient, your firm will avoid potential legal and civil liability. Alternatively, if it is critical to allow their use, then a formal policy and training must be put into place, as well as control measures, to ensure compliance. The other option is to engage a trusted third party to provide a secure solution.
For example, you can allow the use of free machine translation of individual words, sentences without traceable information, information that will otherwise be published or already may be in the public domain, and any anonymized or pseudonymized non-confidential information.
Your policy must explicitly prohibit the translation of unredacted sentences or paragraphs, entire documents, text containing confidential, and personal data.
How to Evaluate Providers
Engaging a translation provider who can provide a secure MT solution among a broader service offering that meets your company’s complete translation requirements may prove to be the most beneficial approach. However, your security evaluation should not end there. If your projects include handling of personal or confidential data, you should include a data security section in your service agreement to ensure that the provider is contractually bound to adhere to proper data handling practices. For example, if your company deals with health-related data, you must ensure that your translation provider adheres to HIPAA privacy rules for PHI (Protected Health Information). Ascertain how they safeguard personal and corporate financial data. One way to do this, even if you are a U.S.-based firm, is to use GDPR as a standard and ask your translation provider about their GDPR compliance. For overall data security, choose a provider who is ISO 27000 or SOC2 certified.
If your company wants to use secure online MT services directly, here are some options:
All of these carry at least ISO 27001 certification or other recognized security certifications.
Further Aspects of Data Security
Aside from machine translation tools, there are other software tools commonly used by language service providers that are important to your data security. Business Management Systems and Translation Management Systems are two systems commonly used by well-equipped service providers.
Business Management System Security
A Business Management System (BMS) stores information about your company and employees who may be interacting with your translation service provider. It may store emails and financial information related to your company’s translation purchases. It must obviously protect credit card information, but you also may not want your competitors to know about your translation activity, therefore, you should expect it to be secure.
Translation Management System Security
A Translation Management System (TMS) handles your translation project content and related data. It will usually house all your translation memory and glossary databases. These are vital assets that may contain confidential corporate information. They also represent a considerable investment across possibly years of translation projects. In the age of machine learning, such high-quality data is inherently valuable as a resource for training a customized machine-translation engine. With this knowledge, you must ensure that this data is secure and will be used solely for your company’s benefit.
A TMS also helps your translation provider manager work with independent translators who may engage on your behalf to complete a translation project. How they configure the TMS can have a significant impact on data security. For example, some TMS tools allow individual translators to use their own machine translation engines, which may or may not be secure. Your translator provider, depending on the tool, can control access to outside machine translation tools while a translator is working on your projects. It is also possible to control downloading or exporting of your confidential data from the system.
One other aspect of BMS and TMS tools is that they may not be hosted on a server controlled and managed by your translation provider rather by the toolmaker itself. To be truly secure, you must be sure that the whole data infrastructure is either ISO 27001 or SOC certified.
How to Protect Your Data
Here is a summary of the steps you should take to secure your data.
|
Risk |
Protective measures |
|---|---|
|
Free MT tools |
• Disable free MT tools in your company |
|
Paid MT tools |
Choose a provider who: |
|
Data transfer |
• Update your IT policies to restrict the transfer of confidential or sensitive data via email |
|
Translation tools |
• Choose a tool that enables you to restrict the use of free MT tools and exporting data |
|
Language Service Provider |
Choose an LSP who: |
If you would like to learn more about MadTranslation’s approach to data security, please email us at sales@madtranslations.com